|
|
| Symbol: AKA:
costa, cos
|
Flybase ID: {Flybase_ID} |
| Synonyms: {Name}
|
{GadFly} |
| Function: {Short_Function} |
{LocusLink} |
| Keywords: {Keywords} |
{Interactive_Fly} |
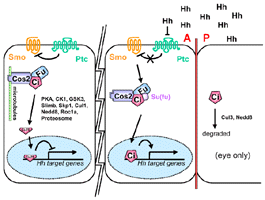
A kinesin like protein involved in Hh signaling
that binds to microtubules and tethers Ci in the cytoplasm.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Repressor of Hh signaling
- cos2w1 (null) clones have increased Ci
levels
- cos23 mutation partially suppresses fu
vein phenotype just like Su(fu)LP (Preat,
1993)
- fu[I]; cos27 flies look like cos27
flies (Preat,
1993)
- fu[II]; cos23 die as late pupae and have
extreme adult cos2 phenotype (Preat,
1993)
|
|
|
- Ci signaling complex
- Cos2-Fu
- Cos-2 co-IP with both Fu and Ci in embryo extracts
(Robbins,
1997, Sisson,
1997)
- Cos-2-Fu-Ci complex associates w/ microtubules
in absence of Hh signalling (Robbins,
1997, Sisson,
1997)
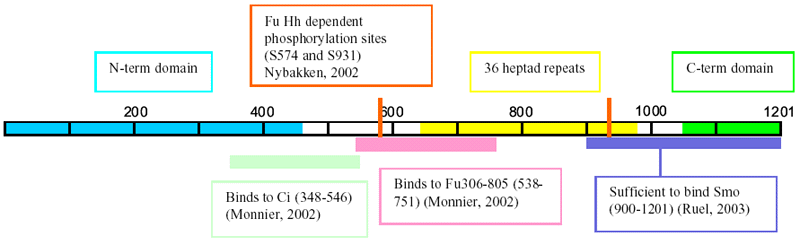
- The C-term domain (aa 421-805) of Fu is necessary
and sufficient to bind Cos2 (Ascano,
2002)
- There appears to be a separate Cos2-Fu species
in gel filtration experiments (Ascano,
2002)
- Cos2-Ci
- forms a complex with Ci via a domain in its
C terminus termed the CORD (Wang,
2000),
- Cos-2 binds microtubules in an Hh-sensitive manner
(Robbins,
1997)
- IPs from ovarian extracts show that Sxl is in a
complex with Fu and Cos2, along with b- and g-tubulin(Vied,
2001)
|
Transcriptional
Regulation |
- Cos2 mRNA levels are uniform throughout discs, however
protein levels are higher in the anterior compartment
(Sisson,
1997)
- Perhaps Ci stabilizes
Cos2 in a macromolecular complex in anterior cells
or Ci heightens translation of COS2 mRNA
(Sisson,
1997)
|
|
|
- The N-terminal (residues 1-450) and C-terminal (residues
1050-1201) regions are predicted to form globular
structures consisting of alternating alpha helices
and beta sheets. The central region (residues 643-990)
contains 36 heptad repeats that are predicted to mediate
the formation of a stable homodimer through a parallel
coiled coil (Sisson,
1997) refs contains additional structural info
- N-term domain similar to motor domains of kinesin
superfamily proteins, but unlikely has motor activity
|
Location (protein
and transcript) |
- Cytoplasmic
- Higher protein levels in the A compartment in imaginal
discs although there is no difference in mRNA expression
(Sisson,
1997)
- Tagged versions of Fu and Cos2 (UAS constructs)
can enter the nucleus, but the rate of entry does
not change with Hh signaling (Methot,
2000)
|
Protein
Modifications and Regulation |
- becomes hyperphosphorylated (on serines) in response
to Hh activity
- Fused is apparently not directly responsible
for the phosphorylation of Cos2, which occurs even
when inactivating mutations are present in the kinase
domain of Fused (Robbins,
1997)
- Fu phosphorylates Cos2 on S572 and
to a lesser extent S931 in a Hh dependent fashion
(baculovirus system) (Nybakken,
2002)
- Phosphorylation is delayed by 15-30 minutes, similar
to Fu (Robbins,
1997)
- response delayed relative to the release of
the complex from microtubules
|
|
|
- N-term domain of Cos2 is similar to motor domains
of kinesin superfamily proteins, but unlikely has
motor activity
|
|
|
- Cos2 mutant clones cross the A/P boundary
(Wang,
2000)
- In a cos2 Su(fu) double mutant en is ectopically
expressed (Wang,
2000)
- Cos2 somatic clones in the anterior compartment
of wing discs express high levels of cytoplasmic Ci
staining and cause mirror-image duplications of the
wing (Sisson,
1997).
|
Overexpression
/ Ectopic expression |
| {Overexpression} |
|
|
|
|