| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Symbol: AKA: cAMP-dependent protein kinase 1, DC0 {Links}
|
Flybase ID: {Flybase_ID} |
| Synonyms: {Name}
|
{GadFly} |
| Function: {Short_Function} |
{LocusLink} |
| Keywords: {Keywords} |
{Interactive_Fly} |
{Summary}
|
|
|
- A serine/threonine kinase involved in signal transduction
- Mediated phosphorylation of Ci promotes its proteolysis (Chen,,
1998)
- PKA catalytic subunit increased proteolytic processing (Chen,,
1998)
- PKI, PKA inhibitor, blocks processing (Chen,,
1998)
- When all Ci’s PKA sites are mutated Ci is not processed (Chen,,
1998)
- Ci that cannot be phosphorylated by PKA (site mut) have increased
transcriptional activity (Chen,,
1998)
- Exogenous PKA can increase further the transcriptional activity of
the ci PKA mut (Chen,,
1998)
- Some results suggest that it is acting in a different pathway (Jiang,
1995, Li,
1995)
|
|
|
- loss of PKA function activates Hh-target genes in the absence of a
functional Hh signal regardless of Ptc concentrations, whereas loss
of Ptc function is unable to activate Hh-target genes at high levels
of constitutive PKA activity (Li et al., 1995). These findings imply,
first, that the ability of Ptc to inhibit activation of Hh-target genes
depends on PKA and second, that PKA does not act on Ptc but on a component
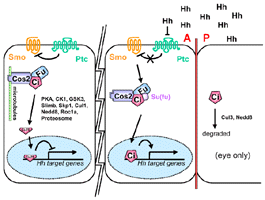
down-stream of Ptc (Figure 8). Recent results show that high PKA activity
cannot counteract the phosphorylation of Fu that depends on the Hh signal
but can be inhibited by Ptc, suggesting that Fu indeed acts downstream
of Hh and Ptc (Therond,
1996). It further follows that PKA does not act on a component between
Ptc and Fu. It is unclear, however, whether PKA acts through Fu or a
component downstream of Fu (taken from Alcedo,
1996)
- role of PKA in Hh signal transduction (Jiang,
1995; Johnson et al., 1995; Lepage et al., 1995; Li et al., 1995;
Pan and Rubin, 1995; Strutt et al.,1995).
- Reduced PKA activity in anterior imaginal disc cells leads to cell-autonomous
induction of dpp, wg, and ptc transcription that is independent of hh
gene activity (Li,
1995)
- Over-expression of PKA can counteract transcriptional induction of
ptc by hh in cells close to the posterior compartment (Li,
1995)
- PKA inhibition leads to increase C-term Ci staining (Hh & Smo
independent) and Hh target gene expression (Smo dependent and somewhat
Hh dependent) (Ohlmeyer,
1997)
- Increase PKA activity can induce ectopic Hh target gene expression
in a manner that requires Smo and Ci activities but does not involve
changes in Ci protein concentrations (Ohlmeyer,
1997)
- Hh signaling in embryos does not depend on cAMP-dependent regulation
of PKA activity (Ohlmeyer,
1997)
- PKA might act on Smo perhaps to uncouple it from the inhibition of
Ptc (Ohlmeyer,
1997)
- PKA antagonizes the Hh signal response (Lepage et al., 1995; Pan and
Rubin, 1995, Li,
1995, Jiang,
1995)
- Hh does not induce dpp and wg transcription by down-regulating PKA
activity (Jiang,
1995)
- PKA represses dpp expression in appendage and eye discs and not needed
for dpp reporter activity (Pan and Rubin, 1995)
- Restricts the expression of dpp, wg, & ptc in imaginal discs (Li,
1995)
- Expressing a dominant-negative form of PKA in the dorsal compartment
(UAS-R*/ap-Gal4) results in ectopic Ci-155 and ectopic expression of
dpp, but no change in col expression (data not shown) (Vervoort,
1999). These results indicate that the presence of Ci-155 is not
sufficient to activate col expression in the anterior compartment, in
conditions where it activates dpp and ptc (Capdevila,
1994; Chen,
1996; Hepker,
1997; Li,
1995).
|
|
|
| {Physical
interactions} |
Transcriptional
Regulation |
| {Regulation} |
|
|
| {Structure} |
Location (protein
and transcript) |
| {Location} |
Protein
Modifications and Regulation |
| {Modifications} |
|
|
| {Related
to} |
|
|
- Constitutively activated PKA catalytic subunit prevents inappropriate
dpp and wg expression but does not suppress Hh signalling (Jiang,
1995) IN CONTRAST TO: hyperactivation of PKA could inhibit the normal
induction of ptc by hh at the AP border (Li,
1995)
- Levels of Ci protein appear to be elevated in clones of cells that
lack PKA function
- PKA(DN) ectopically activates A-P border genes and is a suppressor
of partial-loss-of-fxn hh mutations (Pan and Rubin, 1995)
- The absence of PKA function results in similar phenotypes as those
caused by hh ectopic expression, both of them due to dpp and wg derepression
- Pka clones in the anterior margin transform into bristles corresponding
to the region anterior to vein 3 (Jiang,
1995) whereas ptc clones in similar regions transform into posterior
cells (Tabata, T., 1995). Therefore pka probably does not induce ectopic
en expression, as the absence of ptc, or the ectopic expression of hh,
do. (taken from Sanchez-Herrero,
1996)
|
Overexpression
/ Ectopic expression |
| {Overexpression} |
|
|
| {Reagents} |
|
|
|
|
|