| Symbol: Abbreviation: slimb {Links}
|
Flybase ID: {Flybase_ID} |
| Synonyms: {Name}
|
{GadFly} |
| Function: {Short_Function} |
{LocusLink} |
| Keywords: {Keywords} |
{Interactive_Fly} |
{Summary}
|
{Function/Pathway}
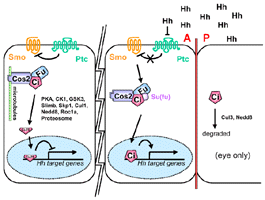
- may target Ci for ubiquitination and hence for cleavage by the proteasome
pathway
- S: proteasome inhibitors block the processing of Ci in tissue culture
cells
|
- Slimb is downstream of PKA activity with regards to Ci processing
(Wang,
1999)
- Ci is more active in PKA clones than in slimb clones (Wang,
1999)
|
|
|
- homologous to S. cerevisiae cdc4 (required for the ubiquitination
of cell cycle regulators
|
- Loss of slmb results in a cell autonomous accumulation of high levels
of both Ci and Arm (Jiang,
1998) and the ectopic expression of both Hh-and Wg-responsive genes
(Jiang,
1998, Theodosiou,
1998)
- Slmb1 acts like a hypomorph and slmb2 and slmbP1493 seem to eliminate
most or all gene fxn
- Slimb mutant cells express dpplacZ at low levels and no ptclacZ or
en (Wang,
1999)
- Ectopic dpplacZ expression is likely due to derepression of dpp, as
formation of Ci-75, dpp’s repressor, is blocked in slimb clones
(Wang,
1999)
- Slmb-, smo- double mutant clones almost completely suppresses slmb
induced outgrowths. Therefore slmb acts upstream of smo (Theodosiou,
1998).
|