| Symbol: AKA: Vn{Links}
|
Flybase ID: {Flybase_ID} |
| Synonyms: {Name}
|
{GadFly} |
| Function: {Short_Function} |
{LocusLink} |
| Keywords: {Keywords} |
{Interactive_Fly} |
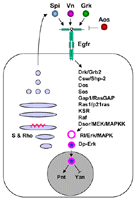
a secreted neuregulin-like molecule that
activates EGFR signaling and is a candidate moledule for establishing the
notum
|
- a secreted neuregulin-like molecule that activates EGFR signaling
and is a candidate moledule for establishing the notum
|
- In wg mutants there is a dramatic and early expansion of vn expression
to include distal cells (Fig 1I), presaging the development of these
cells as an extra notum. However, vn mutants did not lead to expansion
of wg expression (Wang,
2000)
- vn is a target of EGFR signaling in the embryo (Golembo et
al. 1999; Wessells et al. 1999)
- Vn/EGFR signaling regulates Ap expression in a cell autonomous fashion
only early in wing development
- ap expression partially overlaps that of vn in the
second instar (Fig 4I) (Wang,
2000)
- ap can be induced ectopically in ventral clones misexpressing
an activated form of the receptor, EGFRlambdatop4.2
(Fig. 4J) (Wang,
2000)
- Egfrtsla mutant clones generated in the first
instar show autonomous loss of ap expression (Fig. 4K), whereas
clones generated in the second instar express ap normally
(data not shown) (Wang,
2000)
- loss of EGFR activity in whole discs from mid-first to mid-second
instar (with a temperature-sensitive allele) results in complete
loss of ap expression, whereas ap is still expressed
in discs from larvae given a temperature shift slightly later during
the second instar (Fig. 4L–N). (Wang,
2000)
|
- vn is a target of EGFR signaling in the embryo (Golembo et
al. 1999; Wessells et al. 1999)
|
- vn is expressed in the presumptive notum in second instar wing discs
(Simcox,
1996)
|
- hypomorphic vn mutants lack the notum (Simcox,
1996)
- wing primordium fails to grow in vn null alleles and in some
Egfr alleles (Clifford, 1989; Simcox,
1996)
- Inactivating Vn/EGFR activity (with temp sensitive alleles; Egfrts1a,
vntsWB240) during the second instar (a 24 hr period)
caused loss of the notum (Fig. 1 E,F) (Wang,
2000). The wing developed but showed pattern abnormalities characteristic
of vn hypomorphs (Fig 1E) (Wang,
2000). Later shifts during the third instar did not cause loss of
the notum (data not shown) (Wang,
2000). This demonstrates Vn/EGFR activity is required for notum
development in the second instar when wg is required to specify the
wing (Ng,
1996).
- EGFR signaling is needed from mid-first to mid-second instar for wing
development. This was analysised by using a temperature-sensitive allele
Egfrts1a (Wang,
2000)
- In vn null mutants, the initiation of wg expression
is normal and the expression of its target gene optomotor-blind
(omb) (Grimm and Pflugfelder 1996; (Wang,
2000: Fig 1). Later in second instar, wg expression normally expands
to fill the growing wing pouch, however vn mutants wg expression failed
to undergo this expansion (Fig. 4D) (Wang,
2000). A similar defect in wg expression is seen in ap mutants (Ng
et al. 1996) consistent with Ap function being impaired in vn mutants.
- Ap expression is completely absent in second instar vn muant discs
(Fig. 4E&F) (Wang,
2000). This is probably why there is no wing in vn mutants. This
is supported by the demonstration that ectopic ap was capable of rescuing
wing development in vn mutants (Fig. 4G,H). (Wang,
2000)
- In vn mutants, expression of Caup/Ara is lost
(Fig. 2E) and loss of EGFR signaling, in EGFRts clones,
in the medial notum resulted in a loss of Caup/Ara expression
(Fig. 2G). However, clones in the lateral notum continued to express
Caup/Ara (Fig. 2G), suggesting
other factors regulate Iro-C gene expression in these cells at this
stage (Wang,
2000)
- Expression of vn-lacZ is lost in a vnL6/rF264
early third instar mutant wing disc (Wang,
2000)
- when Vn/EGFR signaling is inhibited in the notum by expressing a ligand
antagonist (Vn::Aos–EGF) (Schnepp et al. 1998) under the control
of ptc–Gal4, ectopic wings were induced in ~10% of the flies (Fig.
3G,H). This result demonstrates that presumptive notal tissue can be
transformed to wing by reducing EGFR signaling. However, the transformation
occurred only when EGFR signaling was reduced in a subset of cells,
rather than all cells in the notum (as in a vn mutant) (Wang,
2000)
- this may reflect an indirect requirement
for EGFR activity to also promote wing development (Wang,
2000)
|